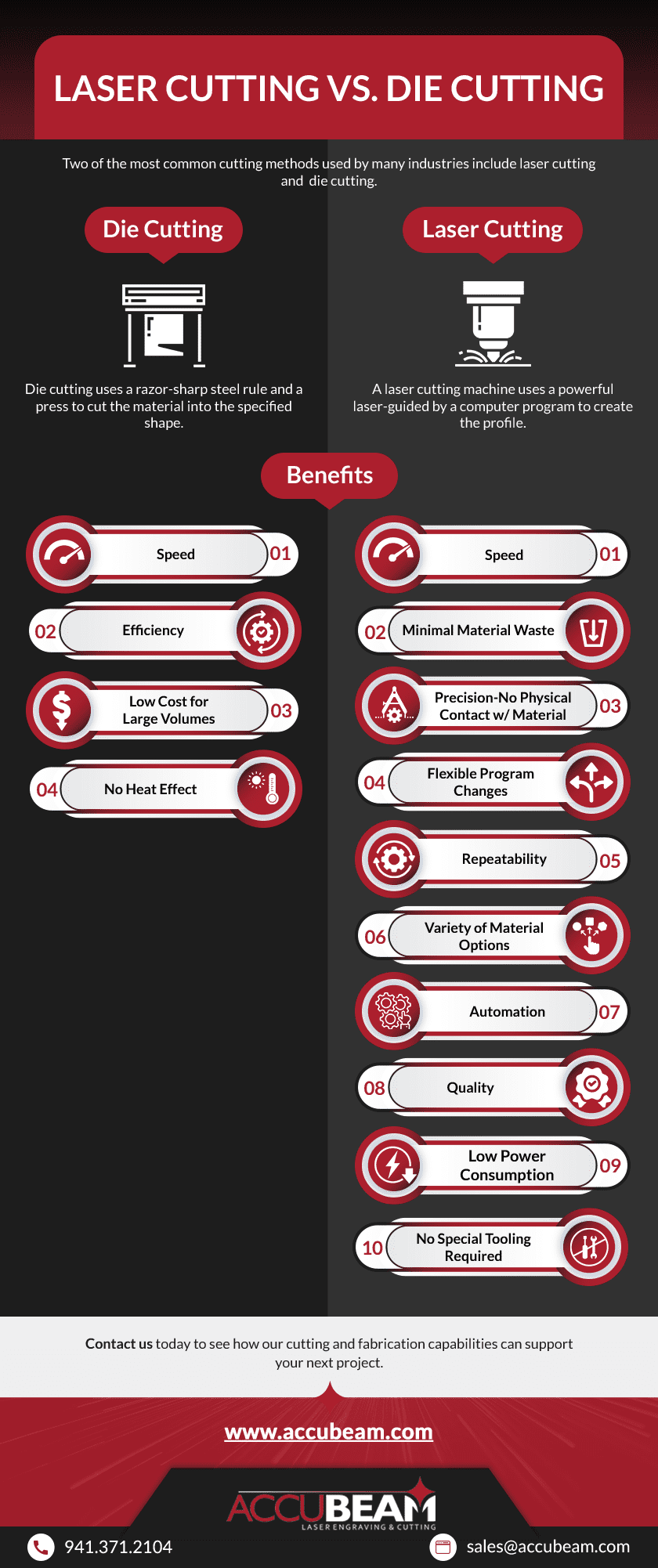
Many industries depend on precision cutting techniques as part of the manufacturing process. Two of the most common cutting methods include laser cutting and die cutting. Die cutting uses a razor-sharp steel rule and a press to cut the material into the specified shape. In contrast, a laser cutting machine uses a powerful laser guided by a computer program to create the profile.
While both methods offer a range of benefits, the right technique for an individual application ultimately comes down to the requirements of the specific project. When comparing laser cutting vs. die cutting, considerations may include materials, cost, volume, and degree of precision. This blog post will dive a little deeper into each technique to help inform process and design decisions.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a fabrication process that cuts materials into extremely precise shapes using a high-powered industrial laser. As the shape emerges, an assist gas blows away any melted material, also known as kerf, from the cut. Laser cutters operate by following a series of instructions derived from a computer-aided design (CAD) file.
Laser cutting sees broad usage across myriad industries, such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, semiconductors, medical, and more. Some of the benefits offered by laser cutting processes include:
- Variety of material options. Intricate shapes can be laser cut from various mediums, such as metal, plastic, synthetics, wood, paper, fabric, and other organic materials.
- Minimal material waste. The high level of accuracy helps to minimize waste during the cutting process.
- Precision. Laser cutting is extremely precise, with an accuracy of +/- 0.1 mm.
- Flexibility. This cutting method can achieve cuts of virtually any difficulty, thickness, or tolerance.
- Repeatability. Due to extremely high precision, laser cutting creates virtually identical cuts across all parts in a production run.
- Speed. Laser cutting requires no time-consuming tool changes and performs cutting operations quickly.
- Automation. The laser cutting process is highly automated, requiring little or no human intervention once programmed.
- Quality. Laser cutting causes no distortion or warping even on thin materials due to the speed of the cut.
- Low power consumption. Compared to a turret punch at maximum capacity that consumes 36 kW of energy, laser cutters typically operate 10 kW of energy or less.
Die Cutting
Die-cutting creates shapes out of softer, more flexible materials like plastic, foam, paper, cork, and others by cutting or perforating with a press. Numerous die cutting methods exist, such as rotary, matched metal, and flatbed. Die cutting is ideal for high volumes, but not recommended for low-volume production or thicker materials. Industries that use die cutting include aerospace, automotive, appliances, shipping, and medical devices, among others.
Benefits of die cutting include:
- Speed
- Efficiency
- Ease of cutting
- Quick turnarounds
- Little production waste
- Low cost
Die cutting machines can also perform multiple functions, such as kiss cutting for adhesives, embossing, laminating, and more.
Your Laser Technologies Partner
The staff at Accubeam Laser Marking has over 40 years of combined experience in lThis blog post offers insight into various considerations when choosing between laser cutting vs. die cutting, such as process benefits and ideal materials. aser fabrication, marking, engraving, and cutting. We work with a diverse range of customers across industries. Contact us or request a quote today to see how our cutting and fabrication capabilities can support your next project.